New insights into the phylogeny of the TMBIM superfamily across the tree of life: Comparative genomics and synteny networks reveal independent evolution of the BI and LFG families in plants
 Gamboa-Tuz, et al. 2018. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 126, 266-278.
Gamboa-Tuz, et al. 2018. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 126, 266-278.
Abstract
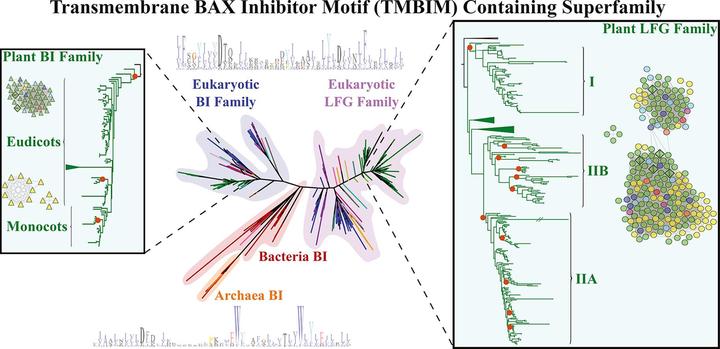
The Transmembrane BAX Inhibitor Motif containing (TMBIM) superfamily, divided into BAX Inhibitor (BI) and Lifeguard (LFG) families, comprises a group of cytoprotective cell death regulators conserved in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, no research has focused on the evolution of this superfamily in plants. We identified 685 TMBIM proteins in 171 organisms from Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya, and provided a phylogenetic overview of the whole TMBIM superfamily. Then, we used orthology and synteny network analyses to further investigate the evolution and expansion of the BI and LFG families in 48 plants from diverse taxa. Plant BI family forms a single monophyletic group; however, monocot BI sequences transposed to another genomic context during evolution. Plant LFG family, which expanded trough whole genome and tandem duplications, is subdivided in LFG I, LFG IIA, and LFG IIB major phylogenetic groups, and retains synteny in angiosperms. Moreover, two orthologous groups (OGs) are shared between bryophytes and seed plants. Other several lineage-specific OGs are present in plants. This work clarifies the phylogenetic classification of the TMBIM superfamily across the three domains of life. Furthermore, it sheds new light on the evolution of the BI and LFG families in plants providing a benchmark for future research.